In geology,
fault is a structure developed due to the slip- off of the rocks from its
original position.
The displacement
of the rocks is due to tensional movement caused by endogenetic force.
During the
displacement of the rocks from its original position, a plane is formed known
as fault plane.
The plane
along which the blocks are displaced is called fault plane.
Fault plane
divides the block into two different parts, i.e footwall and hanging wall.
The block
above the fault plane is called hanging wall and below it is footwall.
MECHANISM OF
FAULTING
Rocks are
considered as elastic body as they can resist some amount of stress applied.
Within the
elastic limit of the rocks, they can resist the stress without being deformed.
The stress/force
mentioned here is tensional stress which is caused due to endogenetic
activities.
But when the
stress applied on the rock exceed its elastic limit, fracture is developed
within the rocks.
And at the
maximum level of stress, fractured block cannot resist more stress and slip off
suddenly from its original position.
The fractured
block displaces along a plane called fault plane and developing a geological
structure called fault.
It is
important to know, that fault is only formed when the fractured block displaces
its original position along the plane.
The sudden
slip–off of the rock releases he energy stored in the rock in the form of
waves.
These waves
are called seismic waves which are responsible causing the earthquake.
This concludes
that, tectonic earthquake is the result of the fault.
TYPES OF FAULT
1) Normal fault:
This geological structure is formed when the hanging wall moves
relatively downward to the footwall.
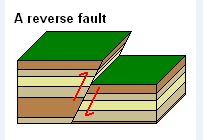
This fault is formed when the hanging wall moves relatively upwards to
footwall.
3) Strike slip fault:
It is also called transcurrent fault.
This fault is formed when two blocks moves laterally side pass each
other.
It is also called left lateral or right lateral depending upon their
movement along the strike.
4) Oblique slip fault:
This fault is formed when two blocks move obliquely pass each other.
This can also occur due to the slip-off of strike slip fault.
- Brodie, Kate; Fettes, Douglas;
Harte, Ben; Schmid, Rolf (29 January 2007), Structural terms including
fault rock terms, International Union of Geological Sciences




Comments
Post a Comment